What is Passivhaus?
Passivhaus is a high-specification energy performance standard for both domestic and non-domestic buildings. A Passivhaus designed building needs to be super-insulated, have very high-performance windows/doors and be extremely airtight. The end result is a space heating demand so low that there is no requirement for a conventional heating system.
Passivhaus is a tried and tested standard that applies to new-build buildings only and has to date certified over 65,000 buildings worldwide. A slightly relaxed standard, known as EnerPHit, applies to retrofit projects where the existing architecture and potential conservation issues mean achieving the Passivhaus standard is unfeasible.
The Passivhaus standard adopts a holistic whole-building design approach alongside a formal certification process that is designed to be achieved without relying on renewables. Specific guidelines are provided for minimum efficiency levels of building elements, infiltration, heat recovery and thermal bridging.
Each certified Passivhaus goes through a quality assurance process which includes a detailed review of the design, construction and on-site installation. This ensures that the exacting levels of thermal performance are met alongside high-quality workmanship.
How is Passivhaus achieved?
A Passivhaus building will typically deliver 70% less heating requirement than Part L building regulations. It can achieve this through:
- Energy-efficient built form and orientation
- Continuous insulated fabric with no thermal bridging
- Very high-performance windows and glazing
- Airtight building envelope with minimal infiltration
- Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery (MVHR)
- Use of solar shading to avoid overheating
In European climates, the space heating load must be below 15 kWh/m2 of usable internal floor area, known as Treated Floor Area (TFA). In addition, the total primary energy demand of the building must be less than 120 kWh/m2. The heating demand can solely be met using a heating element within the MVHR system to maintain a good indoor air quality – without a need for re-circulated air.
In the UK, the Passivhaus target U-values of building elements and ventilation requirements are:
- Opaque building elements (e.g. walls, floors, roofs) <= 0.15 W/m2K
- Windows/doors <= 0.8 W/m2K or <= 0.85 W/m2K once installed
- Thermal bridging <= 0.01 W/m2K
- Fan efficiency <= 0.45 W/m3h
- Heat recovery >= 75%
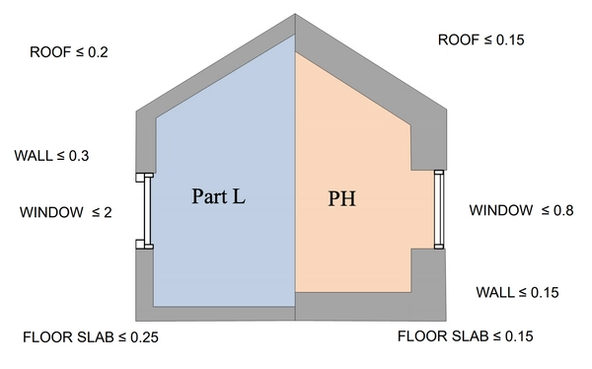
Part L vs Passivhaus U-values
The diagram below highlights the differences in U-values of building elements (measured in W/m2K) between a typical Part L compliant new-build house and the Passivhaus (PH) standard.