What is the difference between infiltration and air leakage?
Infiltration refers to the unintentional ingress of air into a building under natural conditions, while air leakage refers to the uncontrolled movement of air in and out of a building due to a pressure differential across the envelope.
It is not possible to measure infiltration directly; it must be inferred from an air leakage test carried out using either the Low Pressure Pulse (LPP) air test method or a blower door pressurisation fan.
Comparison of Pulse and blower door air pressure test equipment
What is the meaning of air leakage rate, air permeability and air change rate?
An air leakage rate is a specific measure of the amount of air that leaks into or out of a building per unit of time and is the underlying metric used to calculate an air permeability or air change rate. It would typically be measured in cubic metres per hour (m3/h) or cubic feet per minute (CFM).
The air permeability is the air leakage rate normalised by the envelope area of the building, measured in cubic metres per hour per square metre of envelope (m3/h.m2). To calculate the air permeability, you would divide the air leakage rate by the envelope area in square metres.
An air change rate is the air leakage rate normalised by the internal air volume of the building, measured in air changes per hour (ACH, 1/h or h-1). If the entire air within a building or room were to get completely replaced once per hour, this would be an ACH of 1. To calculate an air change rate, you would divide the air leakage rate by the volume in cubic metres.
How do you convert an air leakage result from 4 Pa to 50 Pa?
Within the UK, both the Standard Assessment Procedure (SAP) and CIBSE TM23 define the relationship between a 4 Pa and 50 Pa air permeability result using the following formulas:
These conversion equations were established following the analysis of nearly 300k fan pressurisation tests carried out by the University of Nottingham (research paper).
To convert an air change rate from 4 Pa to 50 Pa, it must first be converted to an air permeability to factor in the geometry of the dwelling (building volume and envelope area).
How do you convert an air leakage result from 4 or 50 Pa to infiltration?
Various methods exist for converting to/from infiltration rates. The Standard Assessment Procedure (SAP) (up to version 10.2) assumes a divide-by-20 rule to estimate the infiltration from a 50 Pa air permeability or air change rate.
The origins of the SAP method are unclear, and it has been found to overestimate infiltration rates in many cases. The current CIBSE Guide A and the proposed Home Energy Model (HEM) method use a lookup table of divisors based on the height of the dwelling and its level of exposure.
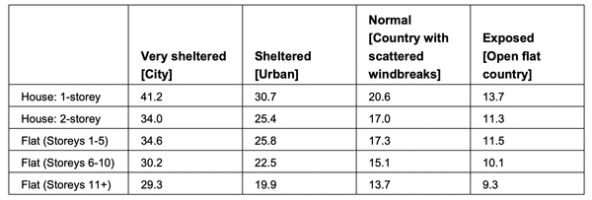
The logic for using different divisors is that infiltration rates will vary significantly based on the prevailing wind and sheltering of the dwelling in question. The divisors are intended to give an average infiltration rate over one year for the specified dwelling types in typical circumstances.
For example, a typical 2-storey house in a suburban location would use the following formulas to calculate the infiltration:
